Co-reporter:Nana Huang, Jinzhou Xu, Hui Zhang, Zheng Xu
Journal of Molecular Structure 2015 Volume 1089() pp:216-221
Publication Date(Web):5 June 2015
DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.02.053
•A sharp decrease in oxygen basicity was observed from Me3SiOEt to Si(OEt)4.•NBO analysis suggest delocalization of oxygen lone pair to adjacent σ∗Si–R is the key factor.•The relative basicity of alkylalkoxysilane was established by a combined IR and DFT study.By a combined IR and theoretical study, the oxygen basicity was found to be sharply decreased from mono- and di-functional alkoxysilanes to tri- and tetra-functional alkoxysilanes. An analysis of the natural bond orbital interactions in Me4−nSi(OMe)n (n = 1–4) and its 1:1 hydrogen bond complex with chloroform indicate that the basicity properties of Si–O–C unit may determined by the competitive hyper-conjugations from the adjacent silicon and carbon centre. The increased contribution from the delocalization of oxygen lone pair to the adjacent Si–R anti-bonding orbitals may be the main origin for decreasing basicity for Si(OEt)4 compared to Me3SiOEt.The basicity of mono-functional alkoxysilanes was found to be remarkably stronger than that of tetra-alkoxysilanes by a combined IR and theoretical studies. NBO analysis suggests that the basicity properties of Si–O–C unit are determined by the competitive hyper-conjugations from the adjacent silicon and carbon centre. The increased contribution from the delocalization of oxygen lone pair to the adjacent Si–R anti-bonding orbitals may be the main origin for decreasing basicity.
Co-reporter:Xin Jiang Feng, Pin Zhan Tian, Zheng Xu, Shao Fu Chen, and Man Shing Wong
The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2013 Volume 78(Issue 22) pp:11318-11325
Publication Date(Web):October 30, 2013
DOI:10.1021/jo401808c
A series of donor–acceptor systems incorporating a carbazole moiety as the donating unit and pyridine moiety as the accepting unit have been designed and synthesized. The spectroscopic and electrochemical behaviors of the carbazole derivatives demonstrate that the carbazole unit interacts with the electron-accepting group through the π-conjugated spacer, thus leading to the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT). The pyridine-substituted carbazole derivatives show significant sensing and coordinating properties toward a wide range of metal cations. Compound S2 exhibits fluorescence enhancement upon association with transition metal cations, and compound V3 shows high selectivity for Cu2+ among this series of materials. DFT calculations indicate the different association abilities of the dyes and the enhancement of ICT upon addition of the metal cations.


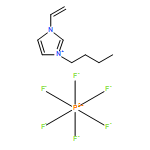
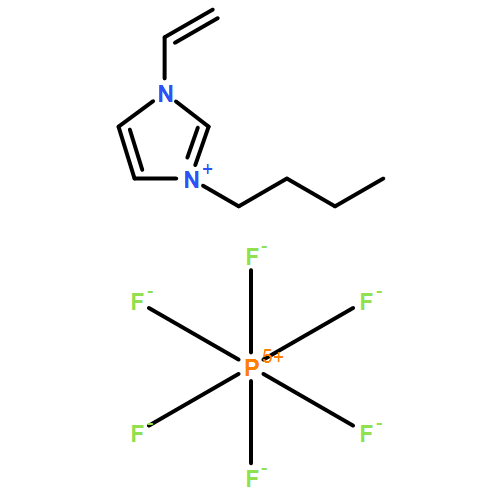
![1,3,2-DIOXABOROLANE, 2-[3,4-BIS(DODECYLOXY)PHENYL]-4,4,5,5-TETRAMETHYL-](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/881300/881209-84-3.png)
![1,3,2-DIOXABOROLANE, 2-[3,4-BIS(DODECYLOXY)PHENYL]-4,4,5,5-TETRAMETHYL-](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/881300/881209-84-3_b.png)
![THIENO[3,2-B]THIOPHENE, 3-BROMO-6-HEXYL-](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/880100/880089-02-1.png)
![THIENO[3,2-B]THIOPHENE, 3-BROMO-6-HEXYL-](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/880100/880089-02-1_b.png)






![Thieno[2',3':4,5]thieno[3,2-b]thieno[2',3':4,5]thieno[2,3-d]thiophene](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/124800/124796-79-8.png)
![Thieno[2',3':4,5]thieno[3,2-b]thieno[2',3':4,5]thieno[2,3-d]thiophene](http://img.cochemist.com/ccimg/124800/124796-79-8_b.png)





