Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Thaksen Jadhav, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Prabhat Gautam, Rekha Sharma, Ramesh Maragani and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: 13076-13086
Publication Date(Web):03 Jul 2014
DOI: 10.1039/C4DT00983E
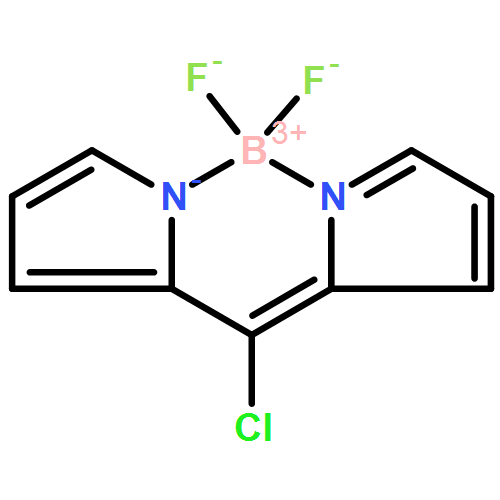
A set of carbazole substituted BODIPYs 2a–2c were designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalysed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. The effects of variation in the donor strength of various carbazoles were investigated by photophysical, electrochemical and computational studies. The electronic absorption spectra of BODIPYs 2a and 2c show charge transfer bands, which show red shift in polar solvents. The BODIPYs 2a–2c are highly fluorescent in nonpolar solvents (emission from the localized state) and poorly fluorescent in polar solvents (emission from the charge transfer state). The photophysical and electrochemical studies reveal strong donor–acceptor interaction between carbazole and BODIPY and follows the order 2a > 2c > 2b. The computational calculations show good agreement with the experimental results. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2a–2c are reported, which exhibit interesting supramolecular interactions. The packing diagrams of 2a show a zigzag 3D structural arrangement, whereas 2b and 2c show complex 3D structural motifs.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Thaksen Jadhav, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Prabhat Gautam, Rekha Sharma, Ramesh Maragani and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: NaN13086-13086
Publication Date(Web):2014/07/03
DOI: 10.1039/C4DT00983E
A set of carbazole substituted BODIPYs 2a–2c were designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalysed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. The effects of variation in the donor strength of various carbazoles were investigated by photophysical, electrochemical and computational studies. The electronic absorption spectra of BODIPYs 2a and 2c show charge transfer bands, which show red shift in polar solvents. The BODIPYs 2a–2c are highly fluorescent in nonpolar solvents (emission from the localized state) and poorly fluorescent in polar solvents (emission from the charge transfer state). The photophysical and electrochemical studies reveal strong donor–acceptor interaction between carbazole and BODIPY and follows the order 2a > 2c > 2b. The computational calculations show good agreement with the experimental results. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2a–2c are reported, which exhibit interesting supramolecular interactions. The packing diagrams of 2a show a zigzag 3D structural arrangement, whereas 2b and 2c show complex 3D structural motifs.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: 13658-13666
Publication Date(Web):05 Jul 2013
DOI: 10.1039/C3DT51374B
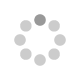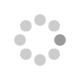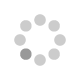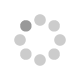
meso-Alkynylated ferrocenyl BODIPYs (3–6) with varying conjugation length have been designed, and synthesized using the palladium catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction of meso-chloro BODIPY with the corresponding ferrocenylethynes. These BODIPYs have been designed to improve the electronic communication between the donor ferrocene, and the acceptor BODIPY. The photonic and electrochemical properties indicate charge transfer (CT) from the ferrocene to the BODIPY. Single crystal X-ray structures of 2′, 3, and 6 show interesting supramolecular interactions. Computational studies were used to study the electronic structure of the BODIPYs.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: NaN13666-13666
Publication Date(Web):2013/07/05
DOI: 10.1039/C3DT51374B
meso-Alkynylated ferrocenyl BODIPYs (3–6) with varying conjugation length have been designed, and synthesized using the palladium catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction of meso-chloro BODIPY with the corresponding ferrocenylethynes. These BODIPYs have been designed to improve the electronic communication between the donor ferrocene, and the acceptor BODIPY. The photonic and electrochemical properties indicate charge transfer (CT) from the ferrocene to the BODIPY. Single crystal X-ray structures of 2′, 3, and 6 show interesting supramolecular interactions. Computational studies were used to study the electronic structure of the BODIPYs.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: 4854-4861
Publication Date(Web):19 Dec 2013
DOI: 10.1039/C3DT53056F
A series of meso arylethynyl BODIPYs (2a–2h) were designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. The effects of the donor on the photophysical properties of the BODIPYs were explored. The DFT optimized structures and crystal structures show the planar orientation of the donor group with respect to the acceptor BODIPY, which favors a high degree of conjugation and induces strong donor–acceptor interactions. The quenching of fluorescence was correlated with the electron donating strength of the donor. The anthracene, pyrene and triphenylamine were found to have a stronger electron donating ability than the p-methoxyphenyl, phenanthrene, 1-naphthalene, biphenyl, and 2-naphthalene moieties. This was further supported by computational calculations and electrochemical analysis. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2d and 2e are reported, which show marvellous supramolecular structures.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: NaN4861-4861
Publication Date(Web):2013/12/19
DOI: 10.1039/C3DT53056F
A series of meso arylethynyl BODIPYs (2a–2h) were designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. The effects of the donor on the photophysical properties of the BODIPYs were explored. The DFT optimized structures and crystal structures show the planar orientation of the donor group with respect to the acceptor BODIPY, which favors a high degree of conjugation and induces strong donor–acceptor interactions. The quenching of fluorescence was correlated with the electron donating strength of the donor. The anthracene, pyrene and triphenylamine were found to have a stronger electron donating ability than the p-methoxyphenyl, phenanthrene, 1-naphthalene, biphenyl, and 2-naphthalene moieties. This was further supported by computational calculations and electrochemical analysis. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2d and 2e are reported, which show marvellous supramolecular structures.
Co-reporter: Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav, Shaikh M. Mobin and Rajneesh Misra
pp: 15803-15812
Publication Date(Web):16 Mar 2015
DOI: 10.1039/C5DT00565E
We report the synthesis of meso enyne substituted BODIPYs by the reaction of 8-chloro BODIPY with terminal alkynes under Sonogashira coupling conditions, and by Pd–Cu catalyzed hydroalkynylation reaction of terminal alkynes, across the –CC– bond of meso alkynylated BODIPYs. The scope of reaction was explored by reacting different meso alkynylated BODIPYs with various terminal alkynes, which results in meso enyne substituted BODIPYs with different substituents. The meso enyne substituted BODIPYs show blue shifted absorption and red shifted emission with large Stokes shift compared to meso alkynylated BODIPYs. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2a, 3b, 4a and 2d are reported. Their packing diagram exhibits extensive intermolecular C–H⋯π, C–H⋯F hydrogen bonding and π⋯π stacking interactions, leading to 1D supramolecular frameworks extending into the complex 3D structural frameworks.
Co-reporter: Bhausaheb Dhokale, Thaksen Jadhav, Shaikh M. Mobin and Rajneesh Misra
pp: NaN15812-15812
Publication Date(Web):2015/03/16
DOI: 10.1039/C5DT00565E
We report the synthesis of meso enyne substituted BODIPYs by the reaction of 8-chloro BODIPY with terminal alkynes under Sonogashira coupling conditions, and by Pd–Cu catalyzed hydroalkynylation reaction of terminal alkynes, across the –CC– bond of meso alkynylated BODIPYs. The scope of reaction was explored by reacting different meso alkynylated BODIPYs with various terminal alkynes, which results in meso enyne substituted BODIPYs with different substituents. The meso enyne substituted BODIPYs show blue shifted absorption and red shifted emission with large Stokes shift compared to meso alkynylated BODIPYs. The single crystal structures of BODIPYs 2a, 3b, 4a and 2d are reported. Their packing diagram exhibits extensive intermolecular C–H⋯π, C–H⋯F hydrogen bonding and π⋯π stacking interactions, leading to 1D supramolecular frameworks extending into the complex 3D structural frameworks.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Thaksen Jadhav, Bhausaheb Dhokale and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: 16052-16060
Publication Date(Web):04 Aug 2015
DOI: 10.1039/C5DT02356D
Two organoboron based fluorophores pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 have been designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction and successfully employed for fluoride and cyanide ion sensing. Pyrazabole 3 acts as a fluorimetric sensor, whereas BODIPY 4 acts as a fluorimetric as well as colorimetric sensor for fluoride and cyanide ions with ratiometric response. The photophysical properties of pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 exhibit good electronic communication between triarylborane and pyrazabole/BODIPY. The single crystal X-ray structure of the pyrazabole 3 shows a chair conformation for the pyrazabole core. The packing in pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 shows interesting supramolecular structures. The computational studies show good agreement with the experimental results.
Co-reporter: Rajneesh Misra, Thaksen Jadhav, Bhausaheb Dhokale and Shaikh M. Mobin
pp: NaN16060-16060
Publication Date(Web):2015/08/04
DOI: 10.1039/C5DT02356D
Two organoboron based fluorophores pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 have been designed and synthesized by the Pd-catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction and successfully employed for fluoride and cyanide ion sensing. Pyrazabole 3 acts as a fluorimetric sensor, whereas BODIPY 4 acts as a fluorimetric as well as colorimetric sensor for fluoride and cyanide ions with ratiometric response. The photophysical properties of pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 exhibit good electronic communication between triarylborane and pyrazabole/BODIPY. The single crystal X-ray structure of the pyrazabole 3 shows a chair conformation for the pyrazabole core. The packing in pyrazabole 3 and BODIPY 4 shows interesting supramolecular structures. The computational studies show good agreement with the experimental results.